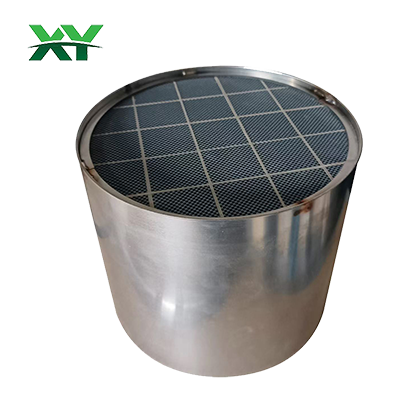
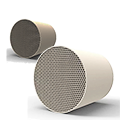
A diesel particulate filter (DPF) combined with a three-way catalytic converter (CFC) is a self-heating filter that reduces black smoke emissions from diesel combustion. Due to the physical characteristics of diesel engines, exhaust contains black smoke and carbon particles. With growing environmental awareness and technological advancements, modern diesel vehicles can significantly reduce black smoke emissions by installing this device to comply with environmental regulations. All carbon particles produced by diesel combustion are intercepted and temporarily stored by the device. The hot exhaust gas from the engine then burns and decomposes the carbon particles stored in the filter, oxidizing them into carbon dioxide, which is then expelled through the exhaust system.
Diesel engine exhaust produces the following substances:
Carbon monoxide (CO): A gas produced when fuel burns in an oxygen-deficient environment.
Hydrocarbons (HC): A general term for compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen. These compounds include unburned or decomposed carbon and hydrogen compounds, fuel vapor, and other compounds in the cylinders. Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Gases formed by the oxidation of nitrogen in the cylinder at high temperatures. They are primarily a mixture of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
Particulate matter (PM): A general term for various solid particles in exhaust gas, typically including heavy metal compounds, sulfates, soot particles (soluble organic matter), and liquid particles coated with fuel.