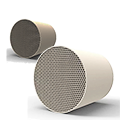
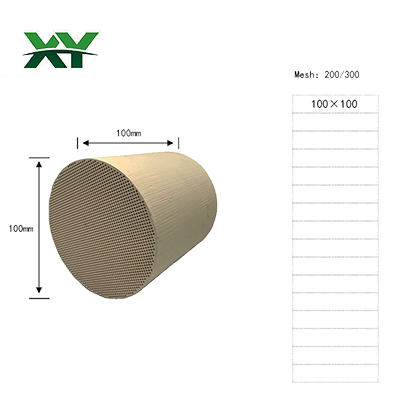
Diesel engine exhaust produces the following substances:
Carbon monoxide (CO): A gas produced when fuel burns in an oxygen-deficient environment.
Hydrocarbons (HC): A general term for compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen. These compounds include unburned or decomposed carbon and hydrogen compounds, fuel vapor, and other compounds in the cylinders. Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Gases formed by the oxidation of nitrogen in the cylinder at high temperatures. They are primarily a mixture of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
Particulate matter (PM): A general term for various solid particles in exhaust gas, typically including heavy metal compounds, sulfates, soot particles (soluble organic matter), and liquid particles coated with fuel.