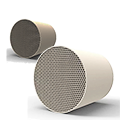
Catalyst carrier principle
Three-way catalytic converters (THCs) convert harmful exhaust gases such as CO, HC, and NOx into harmless carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen through oxidation and reduction. They primarily utilize a three-way catalytic converter (CFC). The carrier component of a CFC is a porous ceramic material installed in a custom exhaust pipe. It's called a carrier because it doesn't participate in the catalytic reaction itself; instead, it's coated with a layer of precious metals such as platinum, rhodium, and palladium. It's the most important off-board purification device installed in a vehicle's exhaust system.
Working Principle
The working principle of a three-way catalytic converter is that when high-temperature exhaust gas passes through the converter, the purifier in the CFC enhances the activity of CO, HC, and NOx, prompting them to undergo a specific oxidation-reduction chemical reaction. At high temperatures, CO is oxidized to colorless, non-toxic carbon dioxide; HC compounds are oxidized to water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide; and NOx is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen. These three harmful gases are converted to harmless gases, effectively purifying the exhaust.
The CFC is similar to a muffler. Its outer surface is made of a double layer of stainless steel sheets in a cylindrical shape. Asbestos fiber felt, a thermal insulation material, is placed between the two thin layers. Inside, a purifier is placed between mesh partitions. The purifier consists of a carrier and a catalyst. The carrier is typically made of aluminum oxide and can be spherical, polygonal, or with mesh partitions. The purifier actually acts as a catalyst, also known as a catalyst. Catalysts are made of platinum, rhodium, or palladium. Spraying one of these metals onto the carrier creates the purifier.
Three-way catalytic converters generally do not require cleaning. If they exhibit severe oxidation, they are simply replaced. Because the operating temperature of a three-way catalytic converter is around 350°C, it is best to avoid any residual liquid water, making cleaning difficult.
In the automotive industry, three-way catalytic converters are important exhaust gas purification devices. The use of their carrier materials not only affects the vehicle's environmental performance.
Three-way catalytic converter carrier materials primarily include ceramic and metal. Ceramic carriers offer lower cost, better thermal stability, and a higher specific surface area, providing more attachment sites for the catalyst, thereby improving catalytic efficiency. Metal carriers offer better thermal conductivity and mechanical strength and are widely used in high-performance vehicles and special operating conditions.